As professionals, employees are eager enough to look for ways to develop their careers and increase their potential for success. One way to do this is by using professional models. It is common to apply the models to the working habit in terms of increasing efficiency and working ability.
In this article, we will explore the importance of professional models in career development, the different types of models available, and how to choose and implement the right one for you.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Different Professional Models
Professional models are frameworks that guide individuals in their career development. They provide a clear pathway for acquiring new skills and knowledge and progressing within a particular field. There are three primary professional models: T-shaped, I-shaped, and M-shaped. Each model has its unique characteristics, benefits, and limitations for employees to apply.
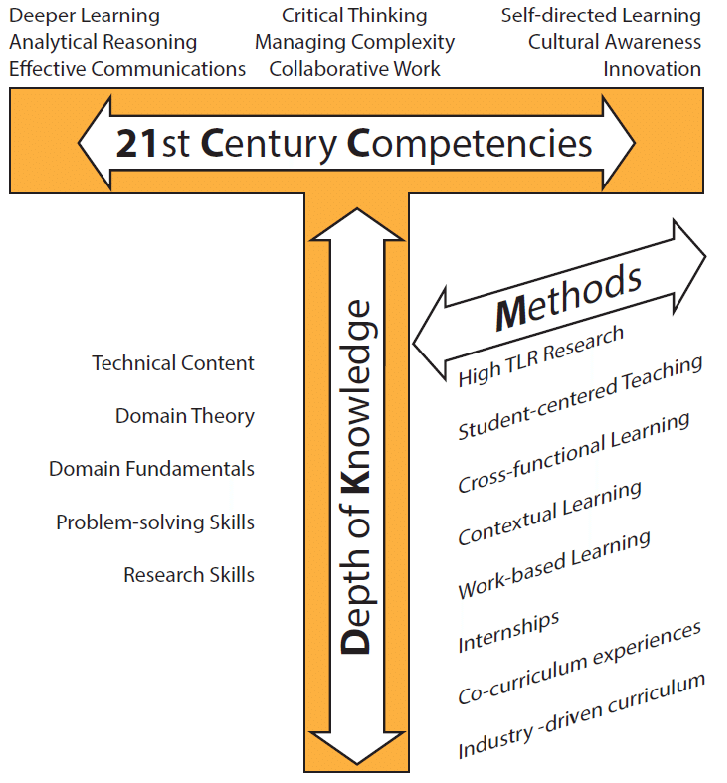
According to a research paper, a T-shaped model is recommended for technology students (Webster & Kopp, 2017).
First, we mention the T-shaped model, which emphasizes depth and breadth of knowledge. Professionals who use this model possess in-depth knowledge and expertise in a specific area, represented by the vertical bar of the “T.” Additionally, they have a broad range of knowledge in related fields, represented by the horizontal bar of the “T.” This model encourages collaboration and cross-functional thinking.
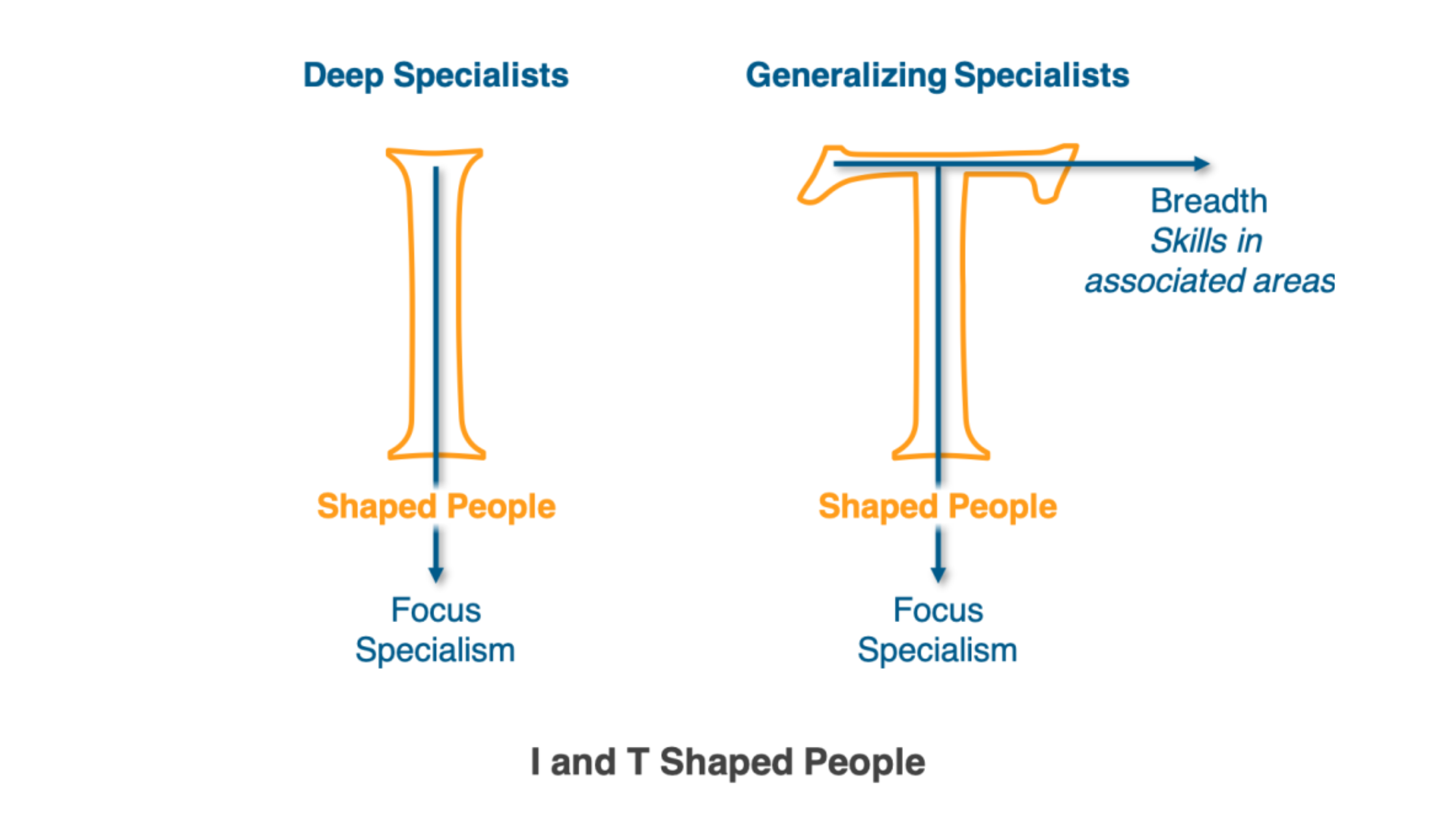
This model is ideal for those who want to become experts (Clayton, 2019).
On the other hand, the I-shaped model emphasizes the depth of knowledge in a single area, represented by the vertical line of the “I.” Professionals who use this model specialize in one area and have deep expertise in that field. This model is ideal for those who want to become experts in a particular area or industry.
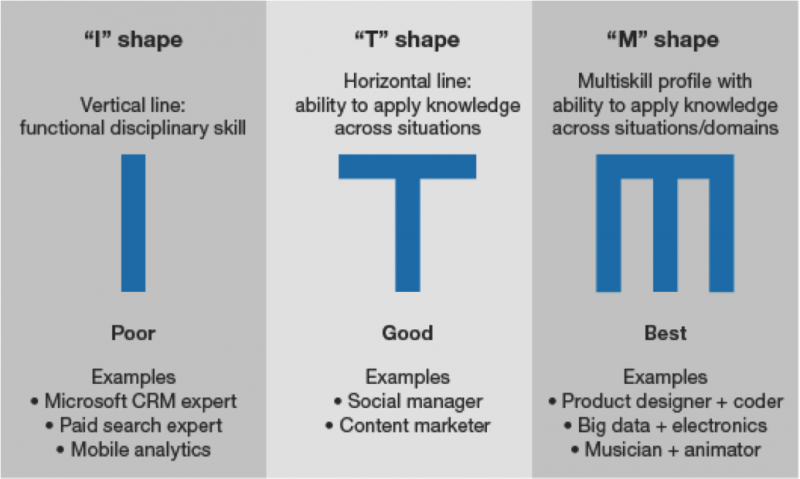
The M-shaped model combines the T-shaped and I-shaped models.
Lastly, the M-shaped model combines the T-shaped and I-shaped models. It emphasizes both depth and breadth of knowledge, as well as cross-functional collaboration. Professionals who use this model have expertise in a specific area but also have knowledge and skills in other related areas.
T-Shaped Model
In detail, The T-shaped model is often used in industries that require collaboration and cross-functional thinking. Employees who use this model have deep expertise in a specific area but also have a broad range of knowledge in related fields. Thus, this model is beneficial for those who want to develop their skills in multiple areas and work collaboratively with others.

Employees who use this model have deep expertise in a specific area and a broad range of knowledge in related fields.
Some examples of professionals who have used the T-shaped model include software engineers who specialize in one language but also have knowledge of multiple programming languages. These marketers specialize in one area but also have knowledge of other marketing disciplines, and designers who specialize in one area are also experts in other design fields.
The benefits of using the T-shaped model include enhanced problem-solving skills, increased flexibility and adaptability, and improved collaboration with others. This model can help professionals stand out in a crowded job market by demonstrating diverse skills.
I-Shaped Model
Mentioning another model, the I-shaped model is often used in industries that require deep expertise in a specific area. It is likely to suit people who use this model, specialize in one area, and have extensive knowledge and skills. Consequently, this model is beneficial for those who want to become experts in their industry or field.

Doctors are one of the careers specializing in I-shaped models.
Some examples of professionals who have used the I-shaped model include doctors specializing in a particular area of medicine, lawyers specializing in a specific area of law, and engineers specializing in a specific type of engineering.
Employees who apply the I-shaped model include the ability to command higher salaries, more significant opportunities for advancement within a particular field, and the ability to become a recognized expert in a particular area.
M-Shaped Model
The last model in this article is the M-shaped model. It is a combination of T-shaped and I-shaped models in terms of having deep expertise in a specific area but also having knowledge and skills in other related areas. This model is beneficial for those who want to develop their skills in multiple areas while still specializing in a particular area.

The M-shaped model enhances various skill sets.
Some examples of specialists who have used the M-shaped model include project managers who have expertise in a specific area but also have knowledge of other project management disciplines, consultants who specialize in one area but also have knowledge of other consulting areas, and executives who have expertise in a specific area but also have knowledge of other business functions.
The M-shaped model can enhance problem-solving skills, increase flexibility and adaptability, and improve collaboration with others. Moreover, it can also help employees stand out in a crowded job market by demonstrating a diverse range of skills and expertise.
Choosing & Implementing the Right Professional Model
3 Methods In Choosing The Suitable Models.
Choosing a suitable professional model can be overwhelming, especially if workers are unsure which one aligns with their career goals. However, considering a few factors can help make the decision easier.

- Self-assessment: Start by assessing your skills, strengths, and weaknesses. Consider what you enjoy doing and where your expertise lies. This will help you identify which model can complement your strengths and interests.
- Identifying your career goals: Consider where you see yourself in the future. Do you want to be a specialist in your field or a generalist who can work in different areas? Do you want to lead a team or work independently? Knowing your career goals can help you choose the model that aligns with your objectives.
- Industry trends: Keep up-to-date with the latest industry trends and demands. Identify which skills are in high order and which models can help you develop those skills.

Once the goals have been identified and fully set, specialists can start implementing the working models into the career development plan. In the following sections, employees can refer to three methods to implement the chosen models.
How to Implement Professional Models
- Developing skills and knowledge: Once you’ve identified the professional model that aligns with your goals, it’s time to start creating your skills and knowledge. This can include enrolling in courses, attending conferences and workshops, and collaborating with colleagues who can share their expertise.
- Networking and collaboration: Building relationships with other professionals in your field can help you expand your knowledge and opportunities. Attend networking events, join online communities, and collaborate with colleagues on projects to build your network.

- Personal development: It’s essential to focus on personal development to improve your skills and knowledge. This can include reading books and articles, listening to podcasts, and participating in online courses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, professional models can be an effective way to advance your career by developing skills and knowledge that align with your career goals. By choosing a suitable model and implementing it effectively, you can achieve success in your field. Remember to assess your skills and goals, keep up-to-date with industry trends, and focus on personal development to make the most of professional models.
References
Clayton, M. (2019, March 25). OnlinePMCourses | Courses to get you set for the project management career you deserve. Online PM Courses. https://onlinepmcourses.com/pmi-agile-practice-guide/
Webster, R. D., & Kopp, R. (2017). Case Study Of A Small Scale Polytechnic Entrepreneurship Capstone Course Sequence. American Journal of Engineering Education (AJEE), 8(1), 35–44. https://doi.org/10.19030/ajee.v8i1.9965
Université Libérale de Paris is proud to be the first liberal arts university for post-graduates. Our liberal arts education is designed with accredited programs through international recognition. Students can self-develop a variety of skills by the A.C.T principle from Paris U.
For a free consultation, you can fill out the form or reach us through social media for further information.




